Application of HBOC from oxygen therapy in cancer
![]() 2024-06-11
2024-06-11
The latest animal studies have found that oxygen inhalation can improve the ability of immune cells to kill tumors, suggesting that routine oxygen inhalation in hospitals may become an adjunct to tumor immunotherapy. The exciting study, which was conducted in collaboration with the New England Institute for Inflammation and Tissue Protection and the University of Pittsburgh, was published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, a subissue of Science.
German physiologist Walburg suggested that cancer production is caused by enhanced cellular glycolysis coupled with reduced oxygen consumption. This, known as the Walburg effect, has been highly controversial in oncology research. However, the rapid growth of tumors consumes more oxygen, and the growth rate of blood vessels often does not match the growth of tumors, resulting in more cells in solid tumors under ischemia and hypoxia.
Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside found throughout human cells, and is an important intermediate for the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenine, adenylate, and glycoadenosine. Exogenous adenosine can directly enter the cardiomyocytes, through phosphorylation to generate adenylate, participate in myocardial energy metabolism. Adenosine can also dilate the coronary blood vessels and increase the blood flow. As a cardiac-protective agent, adenosine is used in the clinic. As for the myocardial protective effect of adenosine, some scholars believe that it was found in the process of studying myocardial ischemia preconditioning.
The concept of ischemia preconditioning was first discovered and proposed by Professor Murry in the United States. Non-fatal ischemia can cause the target myocardium to fight fatal myocardial ischemia injury, and the academic thought is that it should come from environmental adaptation and low oxygen tolerance. In studying the basis of pre-adaptation, scholars found that ischemia leads to the release of large amounts of adenosine from tissue cells, and adenosine through its receptors initiates cellular tolerance.
Under normal circumstances, the body can rely on complete immune mechanisms to effectively monitor and reject cancerous cells. In terms of cellular immunity, T lymphocytes, antibody-dependent cytotoxic cells, NK cells and macrophages have all killing effects on tumor cells. If the cancerous cells themselves or the function of the above immune cells are changed, they may escape the clearance of the body's immune system, and malignant hyperplasia can form tumors. Recently, it have found that adenosine A2A receptor activation of NK cells and other tumor immune cells can promote the body to develop immune tolerance.
Studies have found that cancer cells, like cardiomyocytes, also produce and release adenosine in hypoxia. As a signal transduction molecule, adenosine blocks the tumor immune response, thus protecting cancer cells from T cells and natural killer cells. According to the latest study, the concentration of oxygen in the air is 21%, if breathing 60% oxygen is enough to weaken the tumor hypoxia leading to immunosuppression effect, give a lung cancer and a metastatic breast cancer mouse model to breathe 60% oxygen, can significantly reduce the tumor, improve animal survival rate. It was also found that the environment around the tumor cells became more friendly to the immune cells after oxygen inhalation, allowing more T cells and natural killer cells to penetrate the tumor. After immunotherapy (such as injection of anti-tumor T cells) combined with oxygen inhalation, lung cancer tumor volume reduction in mice was more effective than immunotherapy alone. Because of this study, there is currently a clinical trial in lung cancer patients that is testing a combination of supplemental oxygen and a cancer vaccine.
Although oxygen is indispensable to life, to the human body is toxic gas, long-term breathing pure oxygen to lung injury is very serious, breathing 60% oxygen (precisely, is oxygen pressure is 60 kPa, concentration and gas effect is unrelated, for example on the plateau hypoxia, but oxygen ratio is 21%, but the pressure drop) or the following is safe, can breathe for a long time. Some people may think that if using hyperbaric oxygen, it can increase the effect of oxygen, whether it can achieve a more ideal effect. Of course, it is possible, but hyperbaric oxygen is more toxic, so it can only be used for a short time, the effect is good, need to be proved by experiments.
At present, the exploration of hyperbaric oxygen combined with chemotherapy and radiotherapy, especially the combination of oxygen and radiotherapy (because oxygen itself is a radiosensitizer), can improve the effect of radiotherapy. However, while improving the treatment effect, oxygen therapy also brings many hazards to normal tissues, such as oxygen poisoning.
If pure oxygen for cancer treatment exist congenital unavoidable defects, so we change a way of thinking, since adenosine block radiotherapy and chemotherapy and the autoimmune immune system clearance of cancer cells, and cells release adenosine is a kind of stress response, by controlling the cell stress response to reduce adenosine release, is a new way of cancer treatment? Is there a reagent that has oxygen efficacy fruit (efficient oxygen delivery), reduces stress response and, most importantly, the appropriate dose does not produce adverse effects?
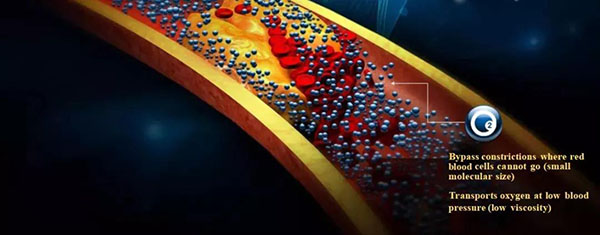
The answer is yes. At present, BIOS, the only bovine source hemoglobin research and development company in China, has developed an ultra-pure and efficient biological oxygen supply agent, which can effectively solve the problems encountered in cancer oxygen therapy.
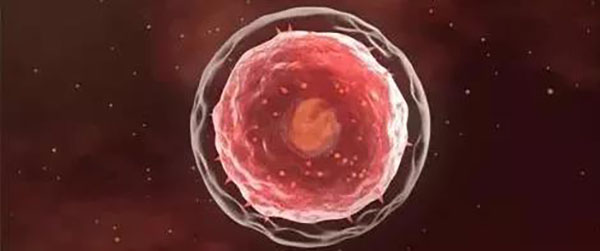
Hemoglobin has an oxygen carrying function in red blood cells, which is composed of four polypeptide chains, and the synergistic effect between subunits determines the oxygen carrying capacity of hemoglobin.Hemoglobin still has the ability to transport oxygen outside the red blood cells, which is in line with the physiological characteristics of the human body and is close to the normal metabolic pathway of the body. However, single infusion has a large toxic reaction on the body. In order to avoid adverse reactions, Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is synthesized by surface modification, intramolecular cross-linking and liposome wrapping. Compared with the hemoglobin modifier directly exposed to the matrix, the coated hemoglobin is less toxic to the body. The volume of Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is much smaller than that of normal red blood cells and has low viscosity. It is easy to effectively perfusion through small blood vessels that cannot be passed by ordinary blood cells, inhibit glycolysis and lactic acid production, and reduce ischemic reperfusion injury. In addition, Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier has good oxygen carrying oxygen release capacity, and its P50 value, Bohu effect and Hill coefficient are similar to whole blood, which can meet the oxygen supply and demand requirements of all organizations.
Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier can not only increase the oxygen-carrying function of blood, but also have a stronger ability to release oxygen to tissues than intraerythrocytic hemoglobin. The perfusion of ischemic brain tissue after Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier infusion into ischemic vessels can increase blood flow and reduce blood viscosity to improve the oxygen supply capacity. The P50 value of Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier (oxygen saturation is 50% oxygen partial pressure) determines the strength of its oxygen diffusion force. The higher the P50 value, the faster the rate of oxygen release to the tissue, and the lower the affinity of oxygen. The lower oxygen affinity of Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier (P50 for Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is 40mmHg and P50 for intracellular hemoglobin is 27mmHg) makes it three times faster than the tissue.
Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier can not only be stored at room temperature for a long time, but also does not need to cross-match before entering the human body. Therefore, it is considered that Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier can be safely and effectively applied in clinical applications.
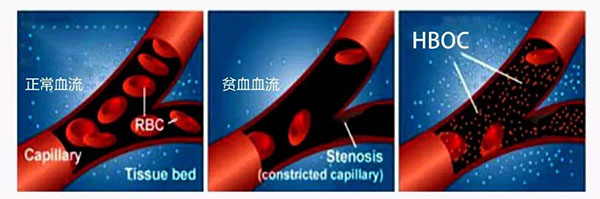
Compared with pure oxygen infusion, fang biological oxygen agent ((Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier) has stable hemodynamic advantage, into the body, Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier circulation in plasma, can quickly improve the blood plasma hemoglobin and total hemoglobin concentration, make oxygen tissues and organs get oxygen perfusion, but also can steadily improve the oxygen transport capacity of red blood cells themselves. Combined with the world's leading protein isolation and purification technology and deremoval process, after chemical modification of Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier and through quality control, it has suitable particle size distribution, which greatly improves the safety of Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier and reduces its adverse reactions in clinical application.
In addition, it is important to note that when the biooxygen agent (Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier) is administered into more than three units of red blood cells or an equivalent dose of Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier (10 units, 250ml / unit), it will theoretically have a constrictive effect on blood vessels. The main reasons for vasoconstriction are the "autoregulation theory" of oxygen without matrix hemoglobin action (infusion of excessive oxygen to the terminal microartery). This is a manifestation of the cellular oxidative stress response, but it is important not that Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier produces oxidative stress, but that "oxidative stress" has an important impact on the release of glandular glands, a key factor in cancer treatment. Through the relationship between oxidative stress status and erythrocyte adenylate metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes, it was found that oxidative stress has a close relationship with cell adenosine release, and some oxidative stress can significantly reduce cell adenosine release.
Push back, we will find an interesting phenomenon: on the one hand, normal infusion can improve immune cells kill tumors and chemotherapy (oxygen is a radiation ensitizer), on the other hand, excessive infusion will produce vasoconstriction caused —— "oxidative stress" and reduce the release of cell adenosine (cell adenosine release negatively associated with autoimmunity) improve anticancer immunity. Despite the excretion of oligomers through the kidney (increasing the risk of renal poisoning), Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier has unparalleled research prospects for cancer therapy.
-

Bios Wins the “Global Hemoglobin Oxygen Carrier Technology Innovation Leadership Award” at the Sullivan New Investment Conference 2025
On August 27, the 19th Sullivan Global Growth, Technology Innovation and Leadership Summit 2025 and the 4th New Investment Conference (hereinafter referred to as “Sullivan New Investment Conference 2025”) was grandly opened in Shangri-La Hotel, Jing ’an District, Shanghai.
2025-08-29
-

Wang Jianfeng, the Secretary of the CPC Changzhou Municipal Committee, met with Mr. Zheng Zhiheng, the Chairman of Bios Biologics
On 28 May 2025, Wang Jianfeng, Party Secretary of Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province, met with Mr. Zheng Zhiheng, Chairman of Bios Biotechnology Co., LTD., Vice Chairman and Executive Director of Chow Tai Fok Jewelry Group Co., LTD., to exchange views on further deepening cooperation.
2025-05-29
-
Yale scientists have successfully revived a pig brain with artificial blood
Recently, the cover of Nature published the latest research from Yale University School of Medicine: scientists at Yale University used an infusion solution to successfully revive the pig brain after 4 hours of death, restoring some cellular and metabolic functions, and maintaining them for at least 6 hours.
2024-08-03
-

A brief history of research and development of red blood cell substitutes
Blood has always been a very important, but very limited medical resource.
2024-08-02